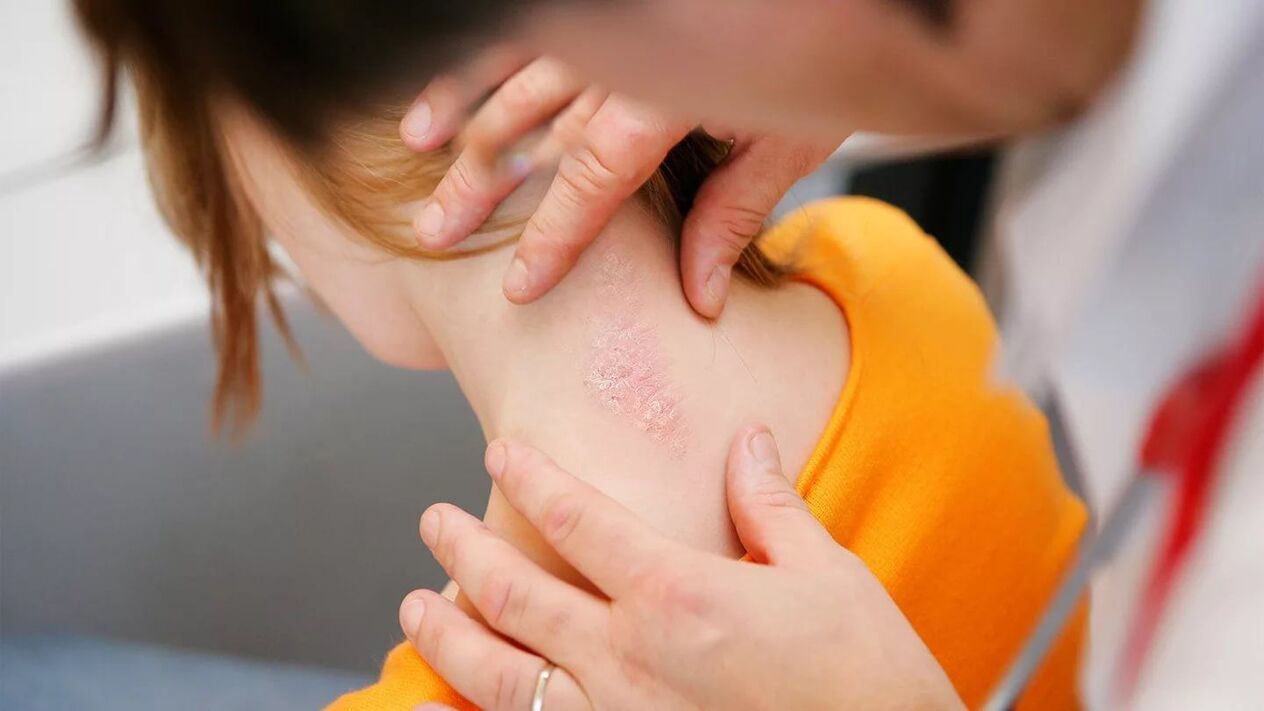
Is psoriasis contagious or not?
When answering the question whether psoriasis is contagious or not, it should be understood that the disease is not transmitted either sexually, or through airborne droplets, or through contact, or through any other means. It is impossible to get infected with it.
Due to the disruption of the exfoliation process of keratinized skin scales, dry patches appear on the body. You cannot die from them, but patients experience serious psychological discomfort because of their appearance.
Causes of psoriasis
It is still not established exactly what causes psoriasis. There are various theories about the development of this disease. Experts tend to believe that damage to the skin and nails can be caused by:
- stress, negative emotional experiences;
- endocrine pathology;
- hereditary predisposition;
- damage to the immune system, which causes the growth and division of epithelial cells to be disrupted.
The cause of autoimmune psoriasis is T-helper immune cells and T-killer cells, normally responsible for protecting the body from tumor cells, pathogenic viruses and bacteria, begin to penetrate the upper layer of the skin. Here they produce substances that activate the inflammatory process. As a result, skin cells begin to divide and multiply rapidly. Proliferation is observed.
The development of psoriasis is also possible with the combined action of several factors from the list below:
- Skin that is very thin and less hydrated (little sebum is produced).
- Frequent contact with irritating compounds - low-quality cosmetics, alcohol solutions, household chemicals.
- Washing your body and hands too often (especially if you use harsh washcloths and antibacterial soap/shower gel).
- Alcohol abuse.
- The development of infectious diseases caused by staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungi.
- Taking antidepressants, lithium carbonate, beta blockers, antimalarials and anticonvulsants.
- Climate zone changes.
- Mechanical injury to the skin.
- Propensity to allergic reactions.
- HIV infection.
Classification of diseases
If you study various photos of psoriasis in the early stages, you will see the difference - there are several types of this dermatological pathology. Depending on the location of the lesion, it occurs:
- Scalp psoriasis (manifested by itching, cracked and bleeding skin).
- Nail psoriasis (the nail plate gradually separates from the bed and becomes painful, red spots form on it).
- Palmoplantar psoriasis (this disease is common only on the soles of the feet and/or palms of the hands).
- Skin psoriasis (dry plaques appear on different parts of the body).
- Psoriasis arthropathy (joints affected).
- Genital psoriasis (disease that affects the skin of the genitals).
Clinical forms of psoriasis:
- Normal or rough. It appears as a small flat pinkish-red papule that is slightly raised above healthy skin. The upper part of the papule is covered with light scales, which begin to fall even with a light touch. If treatment for psoriasis is not started on time, small lesions merge into large ones.
- Exudative. It is more common in people with obesity, hypothyroidism, and diabetes. Symptoms of psoriasis in this form are as follows: bright red papules, with yellow-gray scales visible on them. Plaque affects skin folds - armpits, the area under the mammary glands in women. The patient complains of itching and burning.
- Seborrheic. Psoriasis is observed on the head, behind the ears, nasolabial and nasolabial folds, between the shoulder blades, and on the chest. The borders of the spots are not clearly defined. Silvery yellow exfoliation. If you see a picture of psoriasis on the head, associations will arise with common fungal diseases such as dandruff.
- Palmoplantar. This disease occurs in people aged 30 to 50 years, whose work involves heavy physical work. With this form, a rash may also appear on the body.
- Pustular. Pustular elements are formed on the body. In medicine, an additional type of pustular form is identified - Tsumbusch psoriasis. It can be idiopathic (primary) - blisters appear on the skin, which turn into pustules. The pustule is open and dry. Later, the characteristic scaly rash of the disease appeared on them. And also secondary with tame courses. In this case, pustules appear on the surface of normal psoriatic plaques due to the irritating effect of drugs.
Another type of pustular form is Barber's psoriasis. It only affects the soles of the feet and palms of the hands. Purulent pustules are visualized on the skin. They do not open, and over time they turn into a dark dry crust. Barber's psoriasis is distinguished by the symmetry of the lesions. - Arthropathy (articular). Bad shape. Occurs in patients with skin rashes. It usually occurs five to six years after the first symptoms of the disease appear, if psoriasis treatment is not sufficient. Pathology of the articular system can be different, ranging from mild arthralgia that does not lead to changes in the articular apparatus, ending with deformed ankylosis (joints become completely immobile).
- Psoriatic erythroderma. It is a result of abrasive or exudative psoriasis. Almost all skin is affected. It becomes red, scattered with a large number of dry scales. Body temperature increases, lymph node enlargement (especially femoral and inguinal) is observed. If the patient does not learn how to treat psoriasis, hair loss and brittle nails are possible.
According to the criteria of seasonal relapse, psoriasis is divided into:
- summer;
- winter (most common);
- not sure.
Symptoms of psoriasis
Treatment depends on the predominant symptoms of psoriasis, so at the first appointment the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient and carefully checks the localization of psoriatic lesions.
More often the disease manifests itself in winter. In summer, under the influence of sunlight, the signs of psoriasis may disappear completely. However, with the "summer" pathological form, sun exposure, on the contrary, should be avoided. During an exacerbation, the patient complains of very severe itching. Damage to the nail plate is observed in only 25% of patients.
When there is a scalp disease, the hair is not involved in the pathological process. First, the skin begins to peel. Over time, the rash area can "spread" to the neck area, behind the ears. The inflammatory process is caused by the very rapid division of keratinocytes.
With psoriasis of the hands and feet, the stratum corneum thickens and becomes covered with deep cracks. Photos of psoriasis in the early stages show pustules with transparent contents. Then they turn white and turn into dark scars.
For the nail plate, the most common types of damage are:
- The nail becomes covered with a hole that looks like a puncture mark ("thimble type").
- Nails change color and begin to peel, which resembles a fungal disease. Psoriatic papules surrounded by a red rim can be seen through the nail plate.
Stages of psoriasis
Despite the fact that there is still debate about what psoriasis is and what exactly can trigger its occurrence, the stages of the disease have been well studied. There are three of them:
- Progressive (early). New growths appear on the surface of the skin in the form of rashes, which tend to grow along the edges. They spread to healthy skin and form oval or round plaques. Pink or red spots. No flaky crust yet - just whitish scales. The edges of the lesion are slightly dense. As a result of scratching, a new rash appears.
- Stationary. Occurs one to four weeks after the first symptoms of psoriasis. Plaque becomes lighter. New rashes do not appear, old ones slowly dissolve. The papule heals in the direction from the center to the edge, which is why the shape becomes ring-shaped. The entire surface of the healing wound is covered with flaky white scales.
- Regressive (fading). The color of psoriatic plaques becomes almost indistinguishable from healthy skin. Itching is minimized. Around the lesion, a "Voronov collar" is formed, which is a ring of dense keratin skin layers. If the patient uses a high-quality ointment for psoriasis, the regression stage lasts about a month. Otherwise, the "fading" process may take up to six months.
The task of the patient who has been diagnosed with psoriasis is to keep the disease in remission at all times.
If you find similar symptoms, seek medical advice immediately. It is easier to prevent disease than to deal with its consequences.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
A dermatologist diagnoses psoriasis. This procedure is based on an external examination, assessment of the condition of the skin and nails, and a study of localization of lesions. No additional tests are prescribed for obvious symptoms. If difficulties arise with making a diagnosis, a skin sample is taken from the inflamed area (biopsy), which is studied in the laboratory.
If there is a complaint of joint pain, an x-ray is taken. Blood tests are also ordered to make sure there are no other types of arthritis. To rule out a fungal infection, a test using potassium hydroxide is performed.
How to cure psoriasis
Treatment of psoriasis is complex. It includes:
- general therapy;
- local therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Before determining how to treat psoriasis, dermatologists determine the stage of the disease, its clinical form, and the extent of the process. When prescribing the drug, the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases are taken into account. Usually, the safest medicine for health, characterized by the minimum number of side effects, is chosen first. If they do not ensure the transition of psoriasis to the stage of regression, treatment is adjusted.
Systemic drugs for psoriasis
Medicines taken orally help with moderate to severe psoriasis. This includes:
- Derivatives of vitamin A (retinoids). Reduce the rate of maturation of keratinocytes. Normalizes cell differentiation and maturation.
- Immunosuppressants. Reduce the activity of T-lymphocytes, which triggers an increase in the division of epidermal cells.
- Medicines for the treatment of malignant tumors. Prevents the reproduction and growth of atypical skin cells.
Physiotherapy for psoriasis
Physiotherapy procedures significantly improve the well-being of patients with psoriasis. In some cases, they allow you to completely stop taking the drug. The most commonly used:
- Selective phototherapy. The affected skin is irradiated with UV rays with a wavelength of 280-320 nm. From 15 to 35 procedures are prescribed.
- Photochemotherapy (PUVA therapy). This method involves the use of a combination of photosensitizers internally and long-wave UV irradiation externally. Ultraviolet rays penetrate deep into the skin, and photosensitizers block the DNA synthesis process of skin cells and reduce their rate of division. The duration of the course is from 20 to 30 procedures.
- Laser therapy. Laser beams with different wavelengths are used. The laser ensures accelerated plaque absorption and eliminates scar formation in its place.
- The use of monochromatic ultraviolet radiation. Each lesion is treated in turn with a UV light/laser source. Healthy skin is not affected. This method is optimal if less than 10% of the skin is affected. Treatment duration is from 15 to 30 sessions.
- Electrosleep. There is a mild effect of electrical impulses on the brain for 20-60 minutes. As a result, the patient calms down, the function of the central nervous system normalizes, and the psoriatic plaque begins to resolve.
Ultrasound therapy. It is decongestant, antipruritic and analgesic. Accelerate scar absorption. If necessary, it can be combined with phonophoresis. To achieve a therapeutic effect, 7 to 14 sessions are required. - Magnetic therapy (Betatron device). It has a general healing effect on the body. Relieves inflammation, reduces itching and burning, helps relieve joint pain.
- Treatment with bee venom. Using electrophoresis or an ultrasound machine, bee venom is injected into the body. It is characterized by a resolving and anti-inflammatory effect, normalizing metabolic processes.
- Hyperthermia. Tissue affected by psoriasis is heated with a pad containing a heat mixture to a temperature of 40 degrees. The treatment helps improve the function of the immune system and reduce the negative effects of the disease on the skin.
Ointment for the treatment of psoriasis
According to reviews, the treatment of psoriasis with ointment can achieve excellent results if the drug is chosen correctly. At the first symptoms, non-hormonal formulations are prescribed:
- salicylic ointment (makes the skin soft, relieves inflammation, removes dead epidermal cells);
- anthralin (slows down DNA synthesis, reduces the activity of cellular enzymes, slows down the process of cell division);
- sulfur ointment (disinfects, softens, removes white plaque from lesions);
- naphthalan ointment (relieves itching, relieves pain, normalizes the immune response).
If the treatment of psoriasis with non-hormonal ointments does not give the expected effect, hormonal drugs or strong ointments containing the following glucocorticosteroids are prescribed:
- Hydrocortisone. Relieves congestion and itching. Suppresses the increased activity of leukocytes, preventing their movement into the skin.
- Flumethasone. Helps with the exudative form of psoriasis. It is characterized by significant antiallergic, anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects.
- Triamcinolone acetonide. Has antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects. Shown during the period of exacerbation.
Psoriasis of the scalp occurs in 50% of patients and causes the worst discomfort. If you are sick, you should avoid hair dryers, gels and hair sprays. It is important that the hairpins and combs do not scratch the skin. Otherwise, an epidemic will begin to spread.
Scalp psoriasis treatment is carried out using:
- UV comb (promotes the formation of profiled skin cells from keratinocytes, as existing plaques are reabsorbed).
- Photochemotherapy (UVR combined with Beroxan, Puvalen and Psoralen).
- Medical shampoo (Tana, Nizoral, Friederm tar). It is advisable to buy several different products and replace them. This will prevent addiction.
- Salicylic ointment (apply to the parting, cover the head with cellophane and leave for two hours).
- Hormonal lotions (Belosalic, Elokom, Diprosalic). Contains steroid hormones. Easily applied to the scalp and effectively removes flaking and itching.
- Decoction of Kirkazon (normalizes the process of skin cell division, cleans).
The effect of any scalp treatment is observed after a few weeks, so there is no need to interrupt the course of treatment after a few sessions.
Treatment of psoriasis at home with folk remedies
To cure psoriasis forever at home, if we talk about mild forms of the disease, folk remedies help:
- Herbal tea made from dandelion root, St. wort. St. John's wort or stinging nettle leaves.
- Therapeutic bath with the addition of rope decoction, soap or yarrow.
- Wipe the affected area with cabbage brine, celandine juice, and birch tar.
Compresses based on garlic infusion.
Also, according to reviews, treating psoriasis with hydrogen peroxide can achieve good results. It is necessary to lubricate psoriatic plaques twice a day with cotton soaked in a three percent solution. The duration of the course depends on the severity of the symptoms and can take up to two months.
Diet for psoriasis
Products that are allowed to worsen psoriasis are:
- fruits (apples, apricots, peaches);
- fruit juice;
- vegetables (beets, potatoes, carrots, melons, pumpkins);
- greenery;
- berries (all but red);
- lean meat (beef, veal, turkey, rabbit) - up to 200 grams per day;
- any nuts;
- lean fish;
- fermented milk products, cottage cheese and cheese;
- Wheat bread;
- sea kale.
People with psoriasis should not eat:
- smoked dishes;
- Red fish;
- animal fat;
- eggs;
- pork and duck;
- baked goods.
Drinking coffee, carbonated drinks and alcohol is prohibited. It is advisable to limit your sugar intake. To cleanse the body, it is recommended to carry out fasting days twice a week - vegetables, apples or kefir.
Is psoriasis dangerous?
Psoriasis is a serious but not fatal disease. It reduces the quality of life because it is unsightly. Plaque on the body prevents the patient from working in a team or resting. They often cause limited movement and difficulty performing simple physical tasks. Untimely treatment of psoriasis can cause damage to the organs of vision and joints.
It is impossible to cure psoriasis completely. This is a chronic dermatological disease that must always be kept in a "dormant" state.
Risk group
Risk groups include people who have:
- chronic skin diseases;
- skin injuries;
- disorders of the central nervous system and the autonomic system.
Prevention
To prevent this disease, doctors recommend:
- moisturizes the skin;
- avoid long stays in cold and dry rooms;
- do not take beta blockers and lithium (except in extreme cases), because they trigger psoriasis.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.























